Can You Reverse COPD If You Quit Smoking?
Can You Reverse COPD If You Quit Smoking? A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the leading causes of COPD is smoking, which damages the lungs over time. The question on many smokers' minds is: Can you reverse COPD if you quit smoking? In this article, we will explore the impact of quitting smoking on COPD and provide valuable insights into reversing the disease.
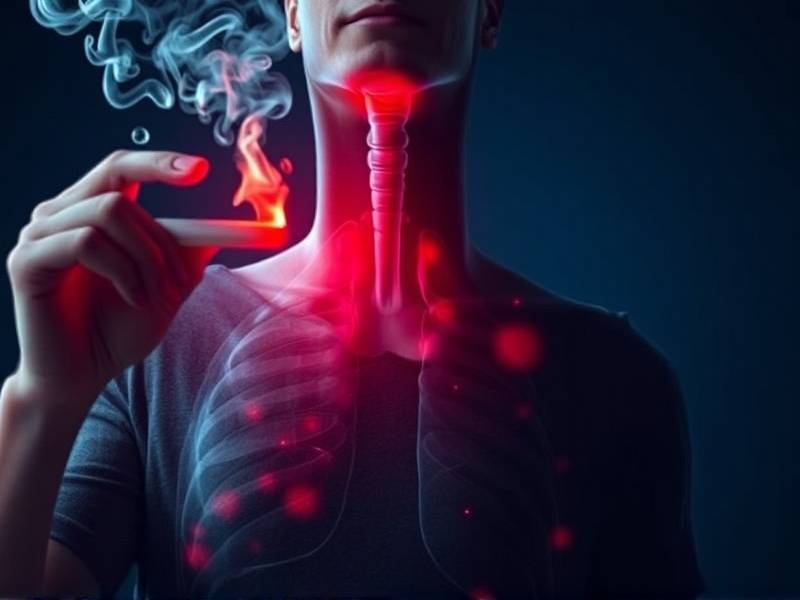
What is COPD? COPD is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by breathing difficulties and airflow limitation. It includes conditions such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Smoking is the most common cause of COPD, as it damages the airways and reduces lung function.

The Role of Smoking in COPD Smoking causes inflammation in the lungs, leading to the production of excess mucus and narrowing of the airways. This inflammation can lead to irreversible damage to the lungs, making it difficult for individuals to breathe properly.
Can Quitting Smoking Reverse COPD? While there's no magic cure for reversing COPD completely, quitting smoking can significantly slow down its progression and improve lung function. Studies have shown that individuals who quit smoking experience several benefits:
- Reduced Inflammation: Quitting smoking reduces inflammation in the lungs, which can help improve breathing.
- Improved Lung Function: Over time, quitting smoking can lead to increased lung capacity and improved airflow.
- Better Quality of Life: Smokers who quit often report improved overall health and well-being.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Quitting smoking can lower the risk of developing other respiratory issues, such as pneumonia or heart disease.
Steps to Quit Smoking If you're considering quitting smoking to reverse your COPD symptoms, here are some helpful tips:
- Seek Professional Help: Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and support.
- Set a Quit Date: Choose a specific date to quit and prepare yourself mentally for the journey ahead.
- Identify Triggers: Understand what situations or emotions trigger your urge to smoke and develop strategies to cope with them.
- Use Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT): NRT can help alleviate withdrawal symptoms by providing a controlled dose of nicotine.
- Stay Motivated: Set achievable goals and reward yourself for reaching milestones along the way.
Conclusion: While quitting smoking may not completely reverse COPD, it can significantly slow down its progression and improve your quality of life. By seeking professional help, identifying triggers, using nicotine replacement therapy if needed, and staying motivated, you can take control of your health and potentially reverse some aspects of your COPD symptoms.
Remember that quitting smoking is a journey that requires patience and determination. With support from healthcare professionals and loved ones, you can overcome this challenge and achieve better lung health in the long run.
