Can You Get Lung Cancer After You Quit Smoking?
The Long-Term Health Impact of Quitting Smoking: Can Lung Cancer Still Be a Concern?
Introduction: The decision to quit smoking is a monumental step towards better health. Many individuals are aware of the immediate benefits such as improved lung function and reduced risk of heart disease. However, the lingering question remains: can lung cancer still develop after someone has quit smoking? In this article, we delve into the complexities of this concern and provide insights based on current research.
Understanding the Risks Post-Quitting Smoking
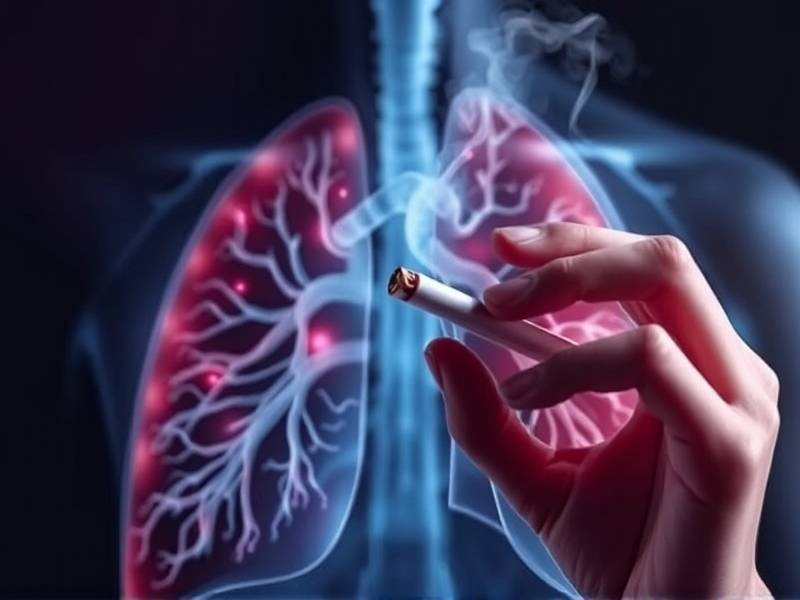
1. The Timeline of Lung Cancer Development
It's important to note that the development of lung cancer is not immediate upon quitting smoking. The time it takes for cancer to develop after quitting can vary greatly among individuals. According to the American Cancer Society, it typically takes 10-20 years for a former smoker's risk to decrease significantly compared to that of current smokers.
2. The Role of Secondhand Smoke and Other Factors
While quitting smoking reduces the risk of lung cancer, it doesn't eliminate all risks entirely. Exposure to secondhand smoke, radon gas, and other environmental factors can still contribute to an individual's risk profile. It's crucial for ex-smokers to be vigilant about their surroundings and take steps to minimize exposure to these hazards.
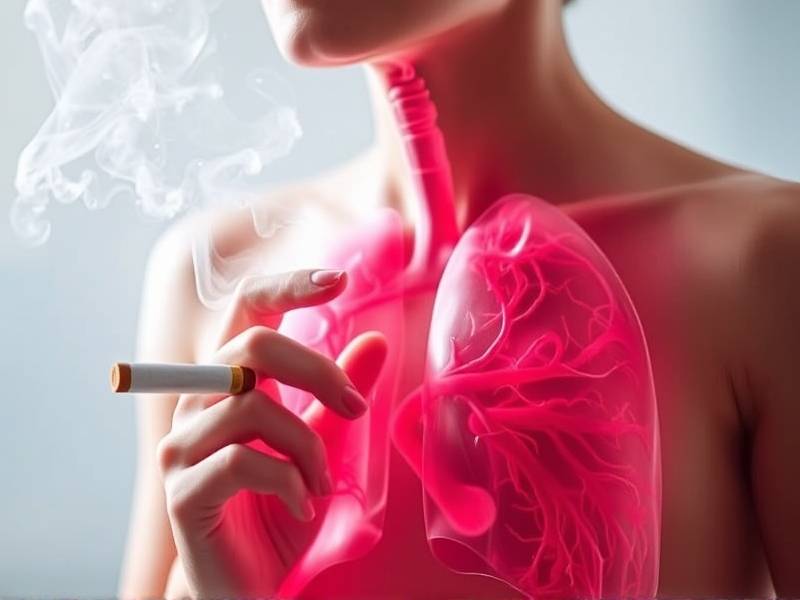
3. The Impact on Risk Reduction Over Time
The good news is that with each year smoke-free, the risk of developing lung cancer continues to decrease. Studies have shown that after 10 years without smoking, a former smoker’s risk drops by half compared to a current smoker's risk.
Can You Get Lung Cancer After Quitting Smoking?
The answer is yes, but the likelihood decreases over time as mentioned earlier. It's essential for former smokers to understand that while they have taken a significant step towards improving their health by quitting, they should not become complacent about maintaining their smoke-free status.
What Can Ex-Smokers Do?
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular medical check-ups with your healthcare provider.
- Lifestyle Choices: Adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Environmental Awareness: Be aware of potential risks in your environment and take steps to mitigate them.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with research and advice from reputable health organizations.
Conclusion: Quitting smoking is a powerful move towards reducing one’s risk of lung cancer and other health issues. While there is always some residual risk, especially in those who smoked heavily for many years, it’s clear that the benefits far outweigh the risks over time. By staying committed to a smoke-free lifestyle and being proactive about one’s health, former smokers can significantly lower their chances of developing lung cancer or any other smoking-related illness.
